What is the difference between Astaxanthin and other antioxidants? What makes astaxanthin so unique?
Astaxanthin is a totally unique antioxidant, because it possesses 3 novel distinctions at once.
Powerful Antioxidant:
Being effective not only on the fat soluble or water soluble part of the cell, Astaxanthin can provide protection for both7. This means Astaxanthin molecule is not only flowing around your bloodstream, but can also penetrate the cellular membrane, which includes the mitochondrial of heart cells, which is one of the reason it’s so beneficial for the heart. Since mitochondrial health is a key factor in aging, supporting mitochondrial health is one of the primary strategies to help slow down the overall aging process.
Astaxanthin is the only carotenoid that is able to cross blood-brain barrier and blood-retinal barrier8, Neuro-protecting the brain and nervous system from the harmful effect of toxins, specifically from smoking, ultraviolet light ionizing radiations, alcohol and medicine. This ability allows its effective delivery, which has huge implications for the health of eye, brain, heart, skin and other parts of the body.
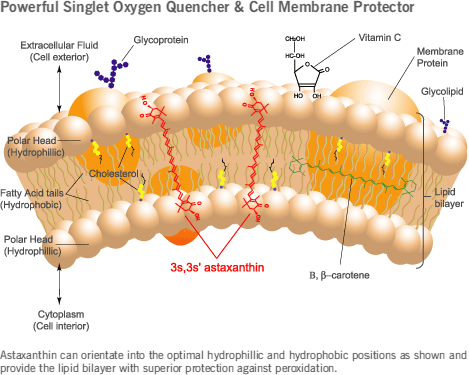
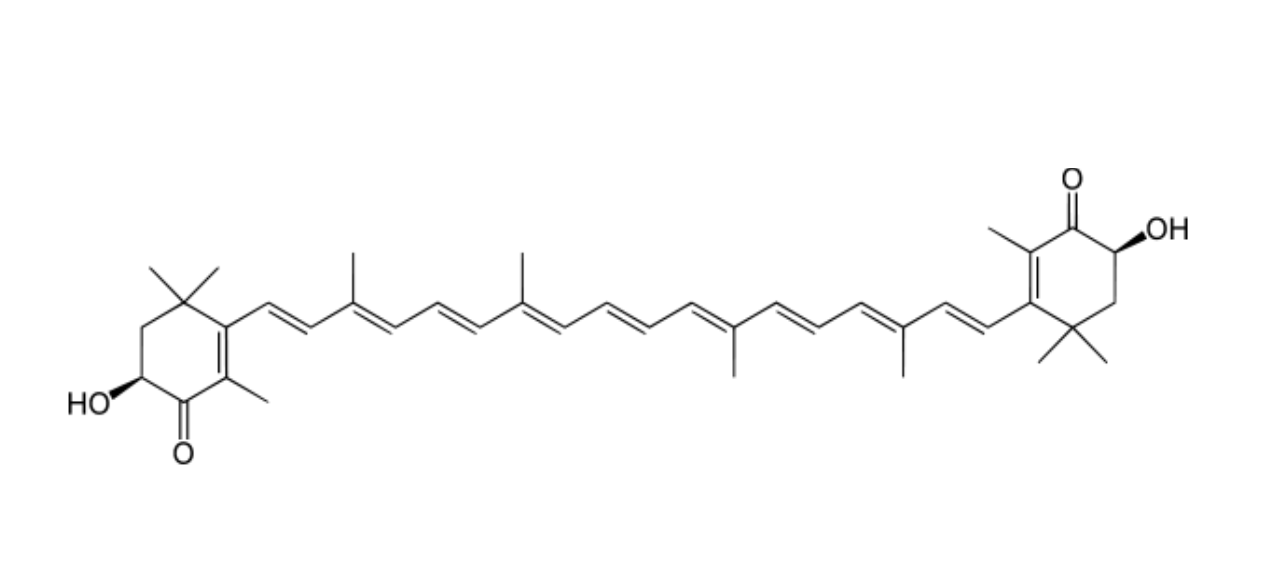
The presence of hydoxyl (OH) and ketone (C=O) moieties on each polar terminal ring along with the extension of conjugated double bond system explain the potency of astaxanthin’s higher antioxidant activity compared to other antioxidants
Safe and Pure antioxidant:
Never a “Pro-Oxidant”
Another key feature of Astaxanthin is that it will not function as pro-oxidant, which means it can never bring destructive oxidation in the body, making it perfect for health-related benefits and performance. Many other antioxidants have the potential to act as pro-oxidants (they cause rather than combat oxidation) when present in sufficient concentration.
This is one of the reasons it is not advisable to go overboard taking too many antioxidant supplements. Astaxanthin, on the other hand, does not function as pro-oxidant (Beutner et al, 2000), even when present in high amounts, which makes it safer and beneficial in protection against different harmful effects of toxins and other free radicals.
“Some of the many things that Natural Astaxanthin can do that beta carotene (and many other carotenoids) cannot:
- Cross the blood-brain barrier and bring antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protection to the brain and central nervous system
- Cross the blood-retinal barrier and bring antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protection to the eyes
- Travel throughout the body effectively to bring antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protection at a high activity level to all the organs and the skin
- Span the cell membranes
- Bond with muscle tissue
- Work as a super-powerful antioxidant and quickly eliminate free radicals and neutralize singlet oxygen.
